Children’s Physiotherapy
What is paediatric physiotherapy?
Paediatric physiotherapy is the treatment and care of babies, children and young people from birth to 19 years.
Paediatric (children’s) physiotherapists bring their specialist skills as physiotherapists and have additional expert knowledge and experience of child development and of childhood conditions.
What do children’s physiotherapists do?
Intervention is based upon an assessment of the child’s needs and the formation of an individual treatment programme.
Children’s physiotherapists recognise the importance of working in partnership with the child, parents and carers to maximise a child’s physical abilities and independence.
Children’s physiotherapists should have a good understanding of …
- child development
- childhood diseases and conditions that may impact on development and well being
- therapeutic interventions that enable and optimise development and well being
- the need to place the child at the centre of planning
- the impact that having a sick or disabled child has on family life
- how to keep children safe
- how to ensure that children and young people make choices
- how to develop their own skills and practice
- how to develop services in line with Government guidance committed to improving quality and life chances for children
Conditions Treated
Children’s physiotherapists treat babies, children and young people with a wide range of conditions. Some are similar to those seen in adults and some are specific to children:
- Acute injuries e.g. fractures, sports injuries
- Burns and plastics
- Childhood cancers
- Congenital disorders e.g. Spina Bifida, limb deficiencies
- Co-ordination difficulties
- Developmental delay
- Learning difficulties
- Neonatal care
- Neuromuscular disorders e.g. Muscular Dystrophy
- Neurological conditions e.g. Cerebral Palsy, Head Injury, Spinal Cord Injury
- Orthopaedic conditions e.g. Talipes, Torticollis, Plagiocephaly
- Respiratory conditions e.g. Asthma, Cystic Fibrosis
- Rheumatological conditions e.g. Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Some parents choose to seek advice and treatment from an independent or private physiotherapist either instead of, or as well as, NHS care. Our paediatric physiotherapist, Damon Khan left the NHS as a Senior Physiotherapist to pursue a career with us. He brings a wealth of knowledge in child development and neurological and musculoskeletal disorders.
For children’s developmental and neurological physiotherapy appointments, Damon will require a 1 hour initial appointment. This is £66 on site at Doncaster or Bawtry, £100 home visit with a 15 minute travel time each way or £120 home visit with a 30 minute travel time each way.
Packages are available for long-term specialist needs.
When booking you will be sent a detailed pre-assessment questionnaire to fill in online. This allows Damon to gather as much information as possible before the appointment, enabling him to focus on the physical assessment during his time with your child. If you would like to discuss your child’s specific needs prior to booking, drop us an email at info@chapmanphysiotherapy.com and we will get Damon to contact you.
Here’s a video of Damon treating Beatrix, one of his long-term clients:
How To Know If Your Child Needs Physio
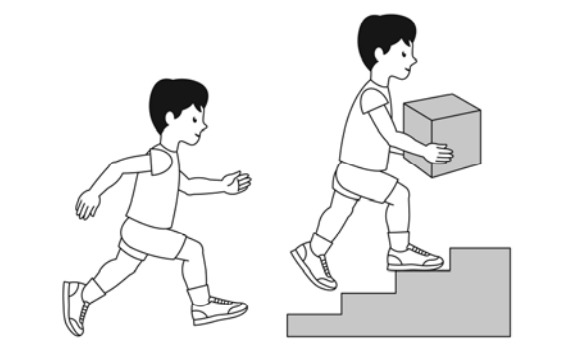
GMFCS Level 1
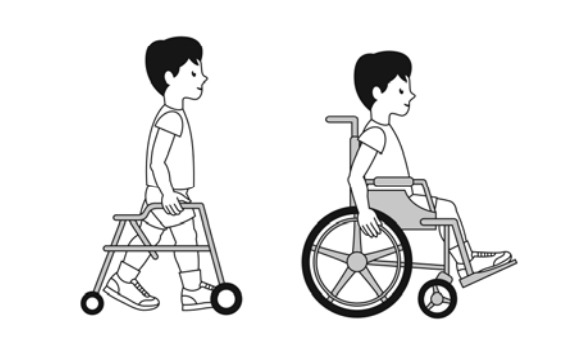
GMFCS Level 2
onto a railing. They may experience difficulty walking long distances and balancing on uneven terrain, inclines, in crowded areas or confined spaces. Children may walk with physical assistance, a hand-held mobility device or used wheeled mobility over long distances. Children have only minimal abil1t’/ to perform gross motor skills such as running and jumping
