Cerebral Palsy
What Is Cerebral Palsy?
The umbrella term given to permanent neurological problems caused by damage to the brain around the time of birth. It is not a progressive condition, but the symptoms and associated problems may change in nature with time, childhood growth and development.
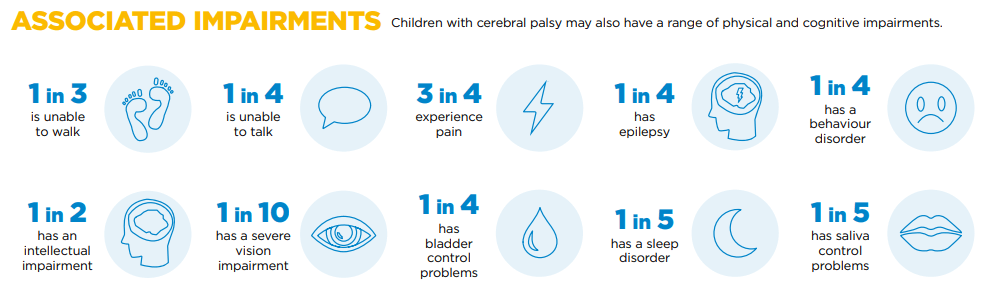
There is huge variation in the severity and type of symptoms, ranging from completely wheel chair bound and dependent on others for support in all activities of daily living to paralympic athletes with mild co-ordination and mobility impairments.
How Common Is It?
In the UK it has been estimated that Cerebral Palsy effect 2 in every 1,000 births.
What Causes Cerebral Palsy?
Around 40% of children with Cerebral Palsy are born prematurely. In many of these children the exact cause is not known, although it has been associated with maternal illness and post natal complications. Some other known contributing factors are:
| Antenatal | Perinatal | Post Natal |
| – Maternal Infections | – Lack of Oxygen At Birth | – Meningitis |
| – Trauma During Pregnancy | – Pre-Term Birth | – Severe Jaundice |
| – Head Injury |
Types Of Cerebral Palsy?
- Spastic (Hypertonia) – Increased tone and reduced muscle function
- Dyskinetic – Problems controlling increased or reduced tone causing movement difficulties
- Ataxic – Difficulties coordinating movements
- Mixed – A combination of the above
Signs & Symptoms
It is difficult to predict the extent of Cerebral palsy or whether or not it will even occur based in the peri natal period (Upto 1 year old).
Symptoms and diagnosis will sometimes not present until later in the infants development and may only become apparent during their development milestones.
- Delays or failure to meet development milestones
- Feeding or swallowing difficulties
- Increased or reduced tone globally or in specific limbs
- Obvious hand preference before 18 months old
- Difficulties with speech, co-ordination or walking
- Learning difficulties
Management
Unfortunately Cerebral palsy is a permanent condition with life long difficulties, it cannot be cured but its symptoms can be managed by maximizing function, controlling pain and tonal changes.
The focus should be on supporting the child’s individual needs to achieve the most fulfilled and independent life. Management of Cerebral Palsy should always be part of an Multi-disciplinary team. This may include:
- Physiotherapists: To stretch, strengthen muscle groups to achieve development milestones, maximize function with use of equipment and prevent muscle contractures
- Paediatricians: Help optimize their medication with muscle relaxants, anti-epileptics and drooling control
- Occupational Therapists: Help support and adapt activities of daily living. Help to provide postural equipment to manage tone effectively
- Orthotics: Provide splints or gaiters to help maintain joint ROM and support walking and other gross motor skills
- Neurologists: Help with diagnosis and specialist management of tone
- Orthopedics: Support with any procedures to release contractures or length tendons
- Speech and Language Therapists: Help support communication and swallowing development or alternate feeding regimes
- Dieticians: Ensure that each child is meeting their nutritional requirements
- Support / Charity Workers: Support with funding and provide opportunities for families connect and meet other children with Cerebral Palsy
How We Can Help
We are excited to announce our new and developing physiotherapy service for Children with Cerebral Palsy, Developmental delay and other neurological presentations.
We are able to work alongside NHS Physiotherapists and Occupational Therapists to help support your child to achieve their individual goals no matter their age or level.
During your initial 1 hour appointment we will listen to your concerns and goals, observe your child’s current abilities and functions. From there we aim to support development of their gross motor skills by increasing muscle strength, helping to stretch tight muscles and prevent contractures, whilst maximizing their confidence and independence.
This will include ‘hands on treatment’ to help facilitate and learn movement patterns, develop individual exercise and stretching programs.
During our initial 1 hour appointment we will listen to your concerns and aims, observe your child’s current movement and functional difficulties. At the practice we can only assess GMFCS scale 3 and above, but we are willing to discuss home visits for more complex needs.
For further information or to register your interest in this service. Please call 01302 321245 or email info@chapmanphysiotherapy.com
How To Know If Your Child Needs Support
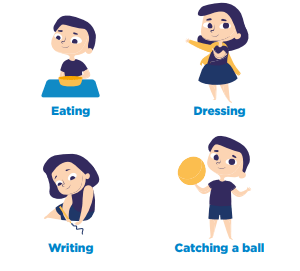
Manual Ability
At least two thirds of children with cerebral palsy will have movement difficulties affecting one or both arms. Almost every daily activity can be impacted.
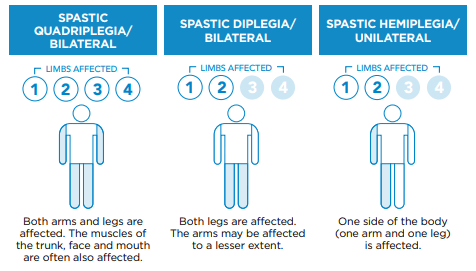
Parts Of The Body
Cerebral palsy can affect different parts the body.
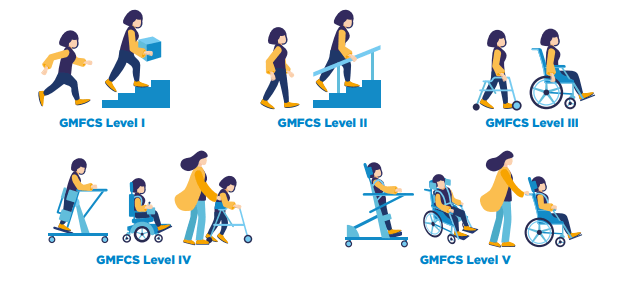
Gross Motor Skills
The gross motor skills (e.g sitting and walking) of children and young people with cerebral palsy can be catergorised into 5 different levels using a tool called the ‘Gross Motor Function Classification System’ (GMFCS) developed by CanChild in Canada.